
This method must be used to calculate exit and entrance losses. The equivalent lengths vary by materials, manufacturer and size. The method of equivalent lengths accounts for minor losses by converting each valve and fitting to the length of straight pipe whose friction loss equals the minor loss. Surface roughness for the piping material (see Pipe Roughness Coefficients) and D i is the inside pipe diameter. The appropriate roughness curve on the diagram isĭetermined by the ratio /D i where, is the specific If the flow is laminar (R 2,100), then f is determined from a Moody Diagram. The friction factor, f, is a function of the relative roughness of the piping material and the Reynolds number, R e.

G = gravitational acceleration, 9.81 m/sec 2 (32.2 L e = equivalent length of pipe for minor losses, m Fluid head loss is added to elevation changes to determine pump requirements.Ī common method for calculating pressure drop is the Darcy-Weisbach equation: Pressure drop, or head loss, is caused by friction between the pipe wall and the fluid, and by minor losses such asįlow obstructions, changes in direction, changes in flowĪrea, etc. Primary factors that will impact these costs and system operating performance are internal pipe diameter (and the resulting fluid velocity), materials of construction and pipe routing. Installed cost of the piping system and operating costs of the system pumps. Pressure drops throughout the piping network areĭesigned to provide an optimum balance between the Practices e.g., boiler feed water and petroleum liquids. May allow greater velocities based on general industry Such as potential for erosion or pressure transientĬonditions may overrule. As stated, this velocity range is considered reasonable for normal applications. This information is then used to determine the minimum inside diameter of the pipe for the network.įor normal liquid service applications, the acceptable velocity in pipes is 2.1 ± 0.9 m/s (7 ± 3 ft/s) with a maximum velocity limited to 2.1 m/s (7 ft/s) at piping discharge points including pump suction lines and drains. Solids concentration, solids density and settling velocity,Ībrasiveness and corrosivity. Recommended fluid velocity for the application and liquidĬharacteristics such as viscosity, temperature, suspended The design flow rates are based on system demands that are normally established in the process design phase of a project.īefore the determination of the minimum inside diameter can be made, service conditions must be reviewed to determine operational requirements such as The primary elements in determining the minimumĪcceptable diameter of any pipe network are systemĭesign flow rates and pressure drops.
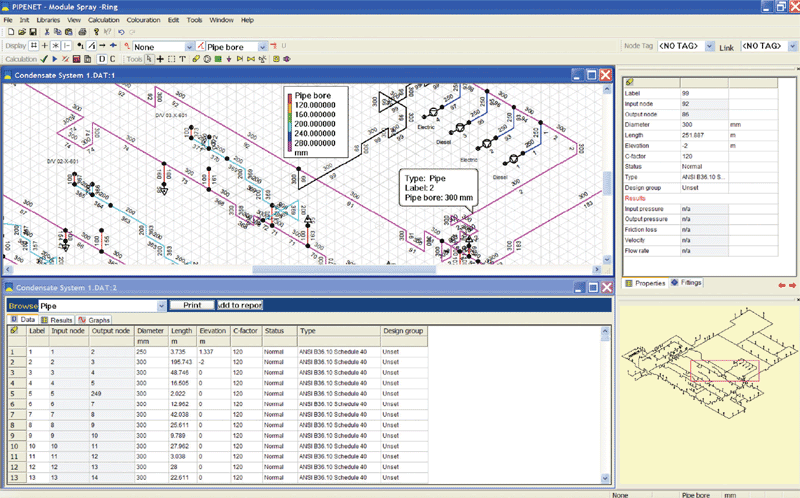
Pressure integrity design determines the minimum pipe wall thickness necessary to safely handle the expected internal and external pressure and loads. Fluid flow design determines the minimum acceptable diameter of the piping necessary to transfer the fluid efficiently. The sizing for any piping system consists of two basic components fluid flow design and pressure integrity design. Pipe Friction drives the pipe size requirements within a fluid flow system and is dependant on the piping system design requirements. Hazen-Williams Method for Pipe Friction and Pressure Drop Pipe Friction Calculations Within Pipe For Fluid Flow


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
